Unit 2: Waves and Electricity - Revision Notes
Comprehensive notes for IAL AS Physics Unit 2, covering theoretical concepts and mathematical applications.
1. Waves and Particle Nature of Light
1.1 Wave Properties
Waves transfer energy without the net transfer of matter. Progressive waves move through a medium, while stationary waves store energy.
- Amplitude: Maximum displacement from equilibrium.
- Frequency (f): Oscillations per second.
- Phase Difference: The fraction of a cycle between two points, measured in degrees or radians.
1.2 Refraction and Polarization
Refractive Index: A measure of how much light slows down in a material.
Snell's Law: Defines the path of light through two media.
1.3 Standing Waves and Interference
Formed by the superposition of two waves of the same frequency and amplitude traveling in opposite directions.
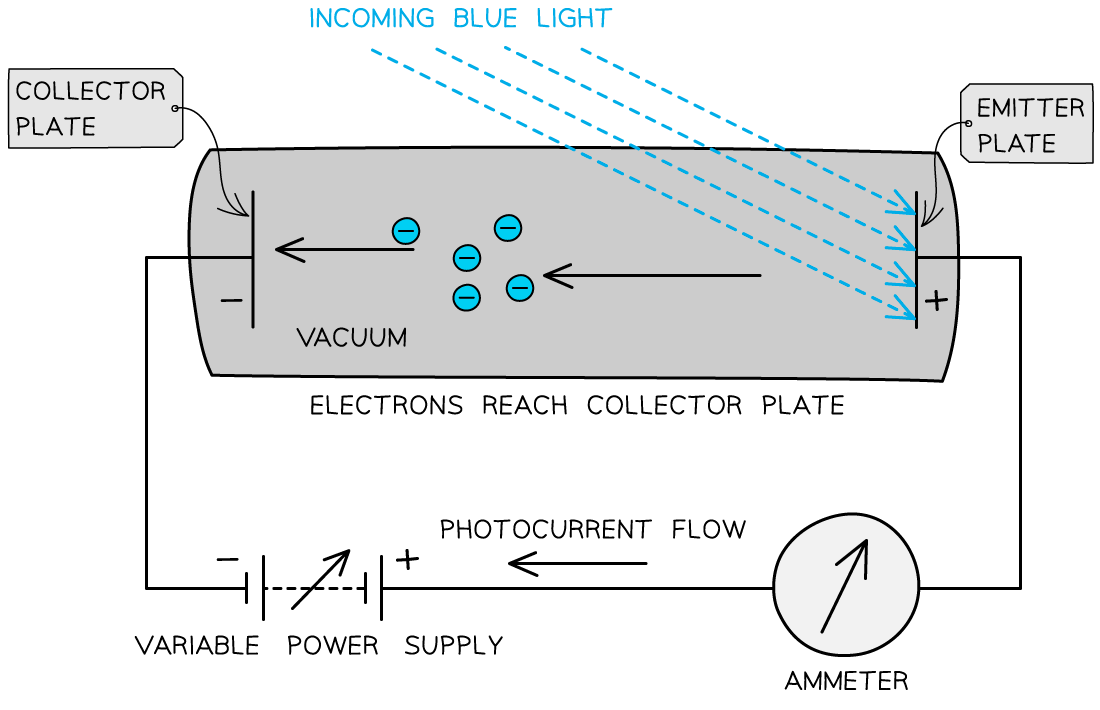
1.4 Quantum Nature: Photoelectric Effect
Light consists of discrete packets of energy called photons. The photoelectric effect demonstrates the particle nature of electromagnetic radiation.
2. Electric Circuits
2.1 Basic Definitions
Current is the rate of flow of charge. Potential difference is the work done per unit charge.
2.2 Drift Velocity
Current in a conductor is related to the number density of charge carriers (), the charge (), the cross-sectional area (), and the drift velocity ().
2.3 Resistivity and Resistance
Resistance depends on the material's geometry and resistivity ().
2.4 Potential Dividers
A simple circuit that uses two or more resistors in series to supply a specific fraction of the input voltage.
2.5 EMF and Internal Resistance
The Electromotive Force (e.m.f.) is the total energy supplied to each coulomb of charge by the source. Terminal p.d. is lower than e.m.f. due to internal resistance ().



YOU MAY ALSO LIKE:
ReplyDelete• Graphing F vs √T:
askfilo.com/waves-graph
• Wave Nature of EM:
gauthmath.com/em-evidence
• Voltage & Potential Difference:
cyberphysics.co.uk/voltage
• Lost Volts & Internal Resistance:
reddit.com/internal-resistance
• Related Video Discussion:
youtube.com/watch-video